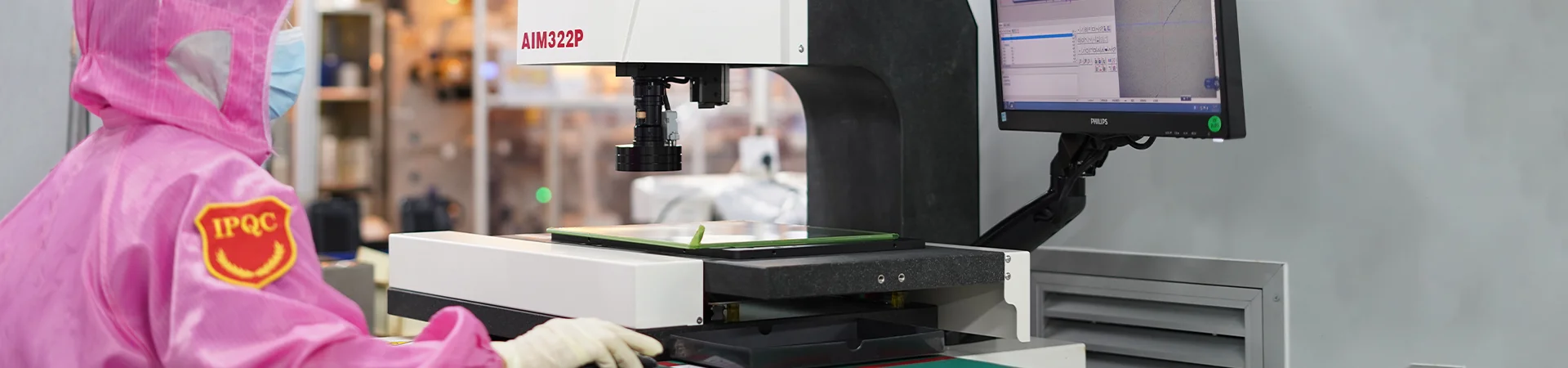
In-process Quality Control For Ceramic PCB Manufacturing
In-process quality control (IPQC) refers to the quality control from the input of raw material into production to the final packaging of products. It is also called manufacturing quality control or quality control during production. IPQC generally adopts random inspection, which involves a random check of the product quality for each process, inspection of the operators of each process, and spot inspection of the content of the control plan.
The Purpose of In-Process Quality Control
IPQC plays a very crucial role in electronics manufacturing, its purposes are as follows:
1. Quality Control
IPQC is responsible for monitoring the product quality during the production process to ensure that all quality standards are met. This includes inspecting the product's dimensions, appearance, functionality, and reliability to ensure that it conforms to specifications and customer requirements.
2. Abnormal Problems Solving
When product quality issues are identified, IPQC must promptly document and report the problems, track the progress of their resolution, and ensure that the issues are effectively addressed. They also need to analyze the root causes of quality problems to prevent similar issues from occurring again.
3. Quality Records
IPQC is in charge of collecting and organizing quality data from the production process, including inspection records, non-conformance reports, quality reports, and more. These records will be used to evaluate product quality and facilitate continuous improvement.
4. Training and Guidance
IPQC is also responsible for providing quality awareness training and guidance to production line employees, assisting them in identifying and avoiding quality issues and enhancing the overall quality level.
How to Create A QC Team?
Creating an effective quality control (QC) process involves several key steps to ensure superior outcomes for products and procedures:
1. Review Industry Standards
Research industry-specific quality standards to set realistic goals. Understand competitors' offerings and consumer expectations. Use market research to determine acceptable quality levels for your products or services.
2. Choose Important Measures
Identify the most critical factors that influence quality. Prioritize factors that align with your business goals. For instance, focus on aspects significantly impacting customer satisfaction and product performance.
3. Set Detailed Expectations
Clearly define each quality standard with specific criteria. Develop accessible guidelines that staff can refer to. Include detailed descriptions and numerical benchmarks to provide clear directives for achieving quality goals.
4. Align Processes with Outcomes:
Develop workflows and procedures that align with quality expectations. Test different operational methods to identify the most effective practices. Select appropriate tools and equipment to support quality control efforts.
5. Develop Training Materials:
Create comprehensive training materials for new and existing staff. Outline quality control steps, manufacturing processes, and service delivery procedures. Include guidance on handling products that don't meet quality standards.
6. Review and Document Data:
Collect and analyze data related to quality standards. Measure product conformity rates, customer satisfaction scores, return rates, and product specification variations. Analyze data to refine the QC process.
7. Gather and Apply Feedback:
Solicit feedback from both customers and staff to improve quality control. Use feedback to adapt quality standards and enhance the QC process. Consider consumer preferences and opinions to refine the definition of a quality experience.
Following these steps, you can establish a robust quality control process that ensures consistent and superior product outcomes, aligning with industry standards and exceeding customer expectations.






















































 HOME
HOME





