Plug-in Components
Plug-in components are electronic components that can be inserted into sockets or holes on a printed circuit board (PCB). These components have leads that can be soldered onto the PCB to create a secure electrical connection. And of course, ceramic PCB also can mount plug-in components on it.
Plug-in components are important for ceramic PCBs because they offer versatility in the design and assembly process. By using plug-in components, designers can easily modify or replace components without having to rework the entire board. This makes it easier and more cost-effective to make changes to the circuitry. In addition, plug-in components can also offer superior performance compared to surface mount components in certain applications. For example, high voltage or high current applications may require plug-in components due to their superior electrical properties. The flexible and reliable solution for electronic circuits makes plug-in components a valuable option for ceramic PCBs.
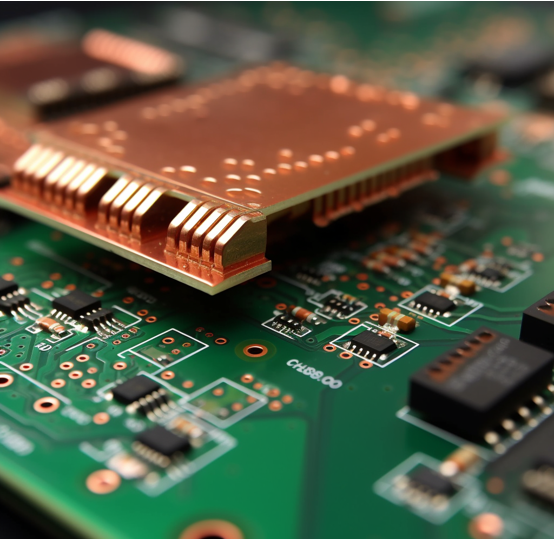
Types of plug-in components
There are many plug-in components in the market, the commonly are:
1. Through-hole components: These components have leads that are inserted through holes in the PCB and then soldered to the opposite side of the board. Examples include resistors, capacitors, diodes, and transistors.
2. Press-fit components: These components are inserted into plated holes in the PCB using a press-fit machine, eliminating the need for soldering. Examples include connectors, sockets, and some power devices.
3. Wire-wrap components: These components have leads that are wrapped around the PCB's plated through-holes, creating a reliable and secure electrical connection. Examples include DIP switches and some types of connectors.
4. SMT components: These components are mounted on the surface of the PCB using solder paste and a reflow oven. While not technically plug-in components, they are often used in conjunction with through-hole or press-fit components to achieve a complete circuit design.
Advantages of plug-in components
Using plug-in components in ceramic PCBs offers several benefits, including ease of assembly and repairability. Plug-in components, such as through-hole and press-fit components, can be easily inserted into the pre-drilled holes on the ceramic substrate, which simplifies the assembly process and helps to reduce production time.
Additionally, plug-in components can be easily replaced or repaired if they fail, which is important in situations where maintenance or upgrades are necessary. This is particularly relevant in industries that require high reliability, such as aerospace, defense, and medical devices, where downtime and failures can have serious consequences.
Moreover, plug-in components provide a high degree of flexibility in design changes, as new components can be easily inserted or removed from the PCB as needed. This allows for quick modifications and customization, making it easier for manufacturers to adapt to changing customer needs and requirements.
The use of plug-in components in ceramic PCBs can help to simplify the assembly process, reduce downtime, and increase flexibility in design changes, making them an important consideration for many industries.
How to assemble plug-in components on ceramic PCBs
Here is a step-by-step guide on how to assemble plug-in components on ceramic PCBs:
Materials and tools we need:
1. Ceramic PCB
2. Plug-in components
3. Soldering iron
4. Solder wire
5. Flux
6. Solder wick or vacuum desoldering tool (if needed)
7. Tweezers
8. Wire cutters
9. Multimeter (optional)
10. ESD-safe work area or mat
Steps:
1. Prepare your work area by setting up an ESD-safe work surface or mat.
2. Identify the correct orientation and placement of the plug-in components on the ceramic PCB, referring to the manufacturer's documentation or datasheet.
3. Insert the plug-in component leads into the corresponding holes in the ceramic PCB. Make sure the leads are straight and properly aligned with the holes.
4. Apply a small amount of flux to the area where the leads meet the ceramic PCB.
5. Heat up the soldering iron to the appropriate temperature for the components being used.
6. Place the tip of the soldering iron onto the lead and the pad on the ceramic PCB. Apply a small amount of solder to the tip of the soldering iron and allow it to melt and flow onto the joint.
7. Once the solder has flowed onto the joint, remove the soldering iron and hold the component in place for a few seconds until the solder cools and hardens.
8. Repeat steps 6-7 for each lead of the plug-in component.
9. Inspect each joint to ensure there are no cold solder joints, bridges, or other defects. Use a multimeter or visual inspection to verify connectivity if necessary.
10. If any defects are found, use solder wick or a vacuum desoldering tool to remove the solder and try again.
11. Once all the components are soldered in place and have been inspected for quality, the ceramic PCB is ready for use.
Note: For press-fit components, the insertion force can be significant and may require a specialized press-fit tool or machine. The manufacturer's documentation or datasheet should provide guidance on the required insertion force and methods for assembly.
Tips for assembling plug-in components
Here are some tips and best practices for assembling plug-in components on ceramic PCBs:
A: Ensure proper alignment and orientation: Before inserting the plug-in component into the PCB, make sure that the pins or leads are correctly aligned with the corresponding holes in the PCB. The component should be inserted perpendicular to the board, with the pins or leads inserted straight into the holes. Improper alignment or orientation can lead to damaged components or non-functional circuits.
B: Use the right tools: Assembling plug-in components on ceramic PCBs requires specific tools, including a soldering iron, solder, and pliers. It's important to use the right tools for the job to ensure that the components are properly installed and secure.
C: Check for damage: Before assembling the plug-in component, check for any damage to the component or the PCB. Any damage can compromise the performance and longevity of the circuit.
Be mindful of the temperature: When soldering the components to the PCB, it's important to use the appropriate temperature to avoid damage to the component or the board. High temperatures can cause damage to the ceramic PCB, while low temperatures may result in poor solder joints.
D: Test the circuit: After assembling the plug-in components on the ceramic PCB, it's essential to test the circuit to ensure that it's functioning correctly. Use a multimeter or other testing equipment to check the circuit for continuity, voltage, and other important parameters.
E: Follow industry standards: Assembling plug-in components on ceramic PCBs should be done in accordance with industry standards and guidelines. Follow the recommended procedures and best practices to ensure a reliable and long-lasting circuit.
By following these tips and best practices, you can ensure that plug-in components are properly assembled on ceramic PCBs, resulting in a functional and reliable circuit.
Quality control
Quality control is essential when assembling plug-in components on ceramic PCBs to ensure that the PCB functions properly and reliably. Some of the key aspects of quality control for plug-in component assembly include:
1) Checking for proper connections: It's important to verify that each plug-in component is properly inserted into the PCB and that all electrical connections are made correctly. Any loose or misaligned components can cause connectivity issues or damage to the PCB.
2) Ensuring secure mounting: It's critical to ensure that each plug-in component is securely mounted to the PCB. If a component is not mounted properly, it can become dislodged or damaged during operation, causing the PCB to fail.
3) Verifying orientation and alignment: Proper orientation and alignment of plug-in components is crucial for the overall functionality of the PCB. Incorrect orientation can result in reversed polarity or incorrect functionality, while misaligned components can cause connectivity issues.
4) Conducting functional tests: After assembling the plug-in components, functional tests should be conducted to ensure that the PCB operates as expected. This can involve running tests to check for proper voltage, current, and signal transmission.
5) By conducting thorough quality control measures during the assembly of plug-in components on ceramic PCBs, manufacturers can ensure that their products meet the necessary performance and reliability standards.
Plug-in components are an essential part of ceramic PCBs, providing numerous benefits such as ease of assembly, repairability, and versatility. The most commonly used types of plug-in components are through-hole components and press-fit components, each with their unique advantages. When assembling plug-in components on ceramic PCBs, it's important to follow the proper steps and best practices, including ensuring proper alignment and orientation and performing thorough quality control checks. By utilizing plug-in components in ceramic PCBs, designers and manufacturers can optimize their performance and functionality. We encourage readers to learn more about plug-in components and their benefits for ceramic PCBs.






















































 HOME
HOME





