Rigorous Testing And Inspection Of Ceramic PCB | BSTCeramicPCB
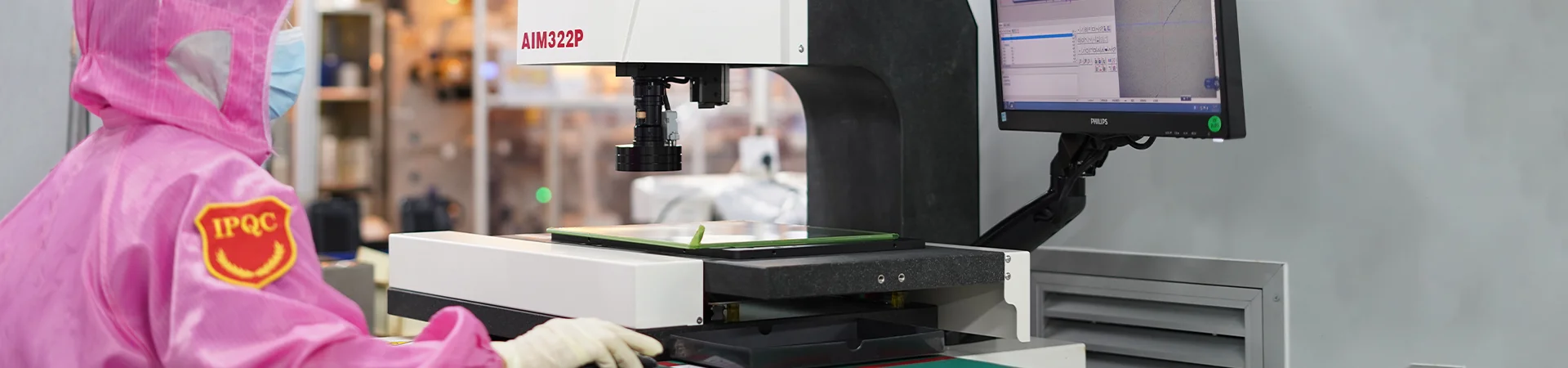
Rigorous Testing and Inspection
Creating a high-quality ceramic circuit board involves a rigorous testing process to ensure its reliability, strength, and functionality. A professional ceramic PCB manufacturer will prioritize these tests to guarantee product quality and high reliability. There are several standards of testing that products go through during the manufacturing process that help determine these attributes before being delivered to customers.
Testing Standards
Institutions such as the Institute of Printed Circuits (IPC) and Société Générale de Surveillance (SGS) are involved in the testing procedures. IPC is accredited by the American National Standards Institute (ANSI) as a standard-developing organization and is known globally for its standards. It regulates the manufacturing, testing and inspection standards of the circuit board industry. It publishes the most widely used acceptability standards in the electronics industry, such as IPC-A-600 (PCB appearance acceptable standard), IPC-6012 (Rigid printed circuit board performance specification), etc.
SGS is renowned for inspection, verification, testing, and certification services. For ceramic PCB, SGS conducts physical characteristics, durability and reliability. ANSI oversees guidelines and standards in the U.S. marketplace to help assure the safety and health of consumers and the protection of the environment. They make sure that PCB manufacturers are building products up to industry standards.
Specific Tests for Ceramic PCBs
Beyond the standard tests mentioned above, a PCB manufacturer should conduct other specific tests on components to verify their quality and durability. These include:
1. Visual Inspection
The first step often involves a visual inspection to identify any visible defects, such as cracks, chipping, or uneven surfaces on the ceramic substrate. This helps ensure the overall integrity of the PCB.
2. Dimensional Measurements:
SGS conducts precise measurements of the ceramic PCB's dimensions, including thickness, hole sizes, and distances between components, to verify compliance with design specifications.
3. Dielectric Strength Testing:
Dielectric strength tests assess the insulation properties of the ceramic substrate. This involves subjecting the PCB to high voltage to determine how well it can resist electrical breakdown.
4. Thermal Cycling Test:
Ceramic PCBs may undergo thermal cycling tests where they are exposed to alternating high and low temperatures to simulate real-world operating conditions. This test helps assess the PCB's ability to withstand temperature variations without cracking or delamination.
5. Thermal Shock Test:
Similar to thermal cycling, thermal shock testing subjects the ceramic PCB to rapid temperature changes, evaluating its resistance to sudden temperature shifts that could cause mechanical stress.
6. Vibration and Shock Testing:
To assess the PCB's durability and reliability under mechanical stress, vibration and shock tests are conducted. These tests simulate the effects of transportation or operational vibrations and shocks.
7. Electrical Testing:
Various electrical tests are performed to ensure the conductivity and proper functioning of the circuit traces and components on the ceramic PCB. This may include continuity testing, resistance measurements, and impedance checks.
8. Environmental Testing:
Ceramic PCBs can be subjected to environmental tests that simulate humidity, salt spray, and corrosive gases to evaluate their performance under different conditions.
9. Solderability Testing:
SGS checks the solderability of component pads on ceramic PCBs by performing solderability tests, ensuring that components can be reliably soldered onto the surface.
10. X-ray Inspection:
X-ray imaging is used to inspect the quality of solder joints and internal connections, helping to identify any hidden defects or inconsistencies.
11. Microscopic Examination:
High-powered microscopes are employed to closely examine the surface and connections of the ceramic PCB, allowing for the detection of microscopic defects that might impact performance.
12. Material Analysis:
SGS might perform material analysis to verify the composition and integrity of the ceramic substrate, ensuring that it meets the required standards.
The Importance of Rigorous Testing and Quality Assurance
Rigorous testing and quality assurance are paramount for ensuring the excellence and reliability of Ceramic Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs). These measures not only enhance the boards' performance and durability but also identify and rectify potential flaws before they reach the market. Through comprehensive testing, manufacturers can optimize performance, guarantee environmental suitability, maintain manufacturing consistency, and adhere to regulatory standards. Such practices not only minimize costs and enhance customer trust but also drive innovation within the field. Ultimately, these processes solidify the position of ceramic PCBs as a dependable and sought-after solution across various industries.






















































 HOME
HOME





