Why Ceramic PCB Is So Expensive?
In the ever-evolving world of electronics manufacturing, more and more designers and engineers are considering choosing ceramic PCB due to their high performance, however, sometimes they are confused Why Ceramic PCB Is So Expensive? After studying the supply chain and cost, I gained some insights. The higher cost of ceramic PCBs can be attributed to several key factors, including raw materials, manufacturing processes, technological requirements, and market dynamics. Next, let us reveal the secret together.
What is ceramic PCB?
Ceramic PCBs, also known as ceramic printed circuit boards, it is a printed circuit boards with ceramic base material, which is highly thermally conductive materials such as alumina, aluminum nitride (ALN), as well as beryllium oxide(Beo), which can make a quick effect on transferring heat away from hot spots and dissipating it over the whole surface.
Let's explore each of these cost factors in detail.
Ⅰ: The first reason is the raw materials.

One of the primary cost drivers in ceramic PCBs is the materials used in their substrate construction. At present, most of the market adopts alumina, aluminum nitride, or beryllium oxide as the base substrate. These ceramic materials offer excellent thermal conductivity, mechanical strength, and electrical insulation properties, but they come at a higher cost compared to traditional PCB materials like FR4. For a example, thin film circuits have high requirements on the surface quality of the substrate, so the purity of the substrate used for thin film circuits is high (a common one is 99.6% pure alumina). At the same time, the high purity of ceramics also contributes an increase cost. The cost of ceramic materials is influenced by factors such as market supply and demand, purity levels, and manufacturing processes.
Ⅱ: The second reason is complex manufacturing processes
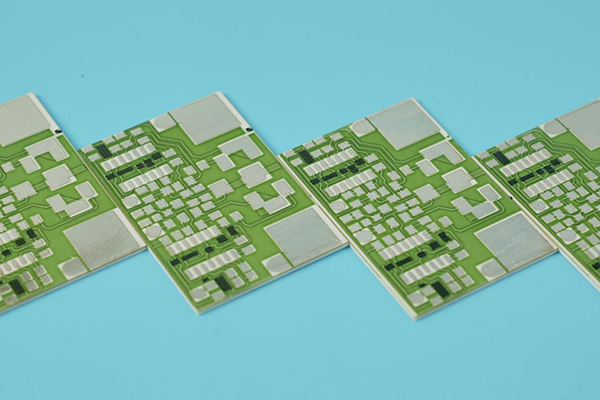
The manufacturing processes involved in ceramic PCB production are more complex and specialized compared to traditional PCB manufacturing. Ceramic PCBs require precise techniques such as thick-film or thin-film deposition, high-temperature sintering, and laser drilling, which demand specialized equipment and skilled technicians. These complex manufacturing processes contribute to higher production costs, including investment in advanced machinery, energy consumption, and labor.

Ⅲ: The third reason is technical requirements
Take the thick film ceramic PCB as an example, the screen printing method used in thick film resistors is to stick a layer of silver palladium electrodes on the ceramic substrate, and then print a layer of ruthenium dioxide between the electrodes as the resistor. The resistive film of a thick film resistor is usually thicker, about 10μm. Thick film resistors are the most commonly used resistors at present, but because it is difficult to control the resistance accuracy and error, the technical requirements for operating workers are extremely strict, resulting in increased costs.
Ⅳ: The fourth reason is research and development
Ceramic PCBs are a product of continuous research and development efforts to enhance their performance and reliability. Innovations in ceramic materials, manufacturing techniques, and design optimization require significant investments in research and development. These costs are eventually passed on to the consumers, contributing to the higher price tag of ceramic PCBs.
Ⅴ: The fifth reason is market supply and demand
The dynamics of market supply and demand also play a role in the pricing of ceramic PCBs. The demand for ceramic PCBs has been steadily increasing due to their unique properties and suitability for high-performance applications. However, the supply of ceramic materials and specialized manufacturing capabilities may be limited, leading to higher prices. Additionally, market conditions and fluctuations in material prices can impact the overall cost of ceramic PCBs.
The Value of Ceramic PCBs
While ceramic PCBs may come with a higher price tag, it is essential to consider their value and the benefits they offer. The exceptional thermal conductivity, mechanical strength, and electrical insulation properties of ceramic PCBs make them indispensable in applications requiring high performance, reliability, and durability. These specialized circuit boards excel in demanding environments, such as aerospace, automotive, power electronics, and high-power-density designs. The ability to handle high temperatures, resist corrosion, and maintain stability under harsh conditions justifies the investment in ceramic PCBs.
Conclusion
Ceramic PCBs offer unparalleled thermal conductivity, mechanical strength, and electrical insulation properties, making them a preferred choice for high-performance electronic systems although it is expensive. If you are looking for a complex ceramic PCB manufacturer, try to email us: sales@bstceramicpcb.com






















































 HOME
HOME